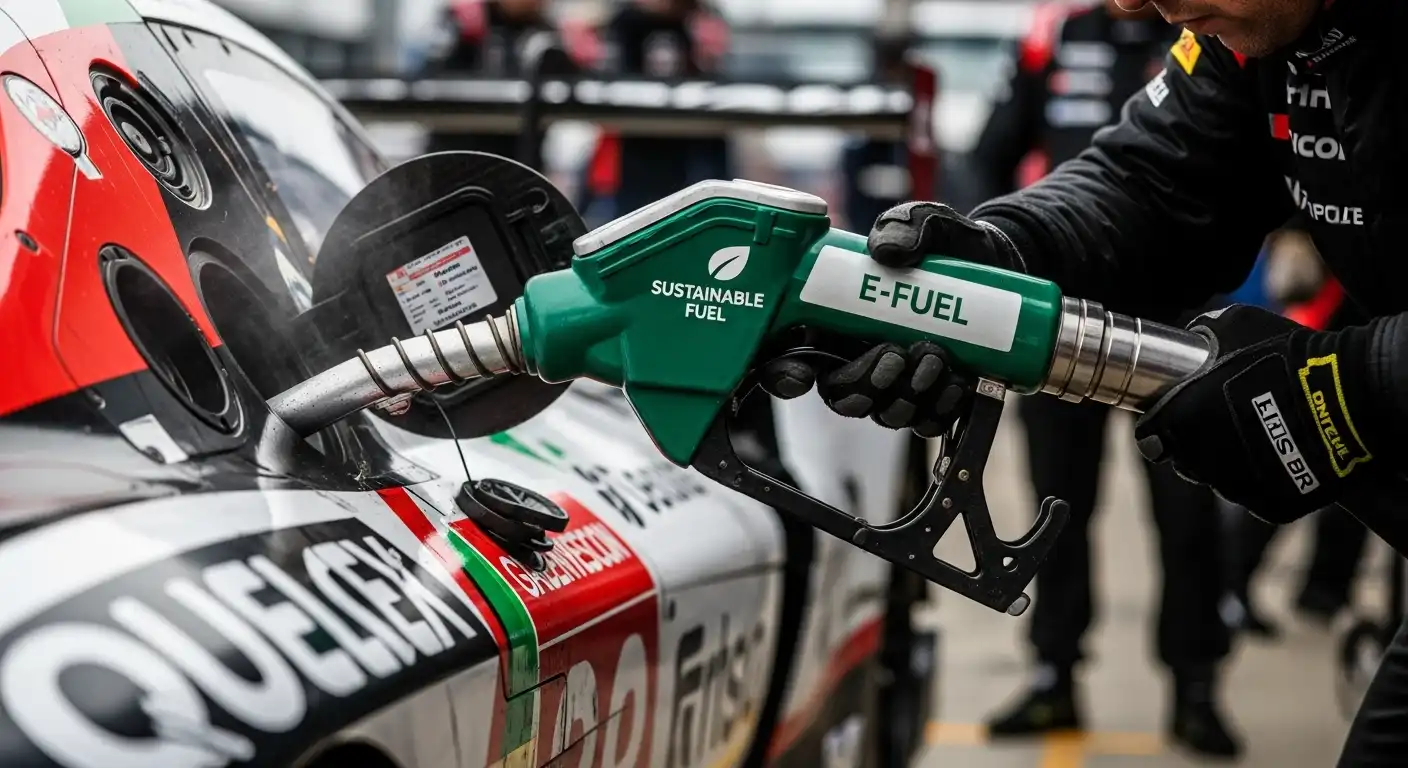
What are synthetic fuels (e-fuels)?
Synthetic fuels are produced by combining captured carbon dioxide with hydrogen made from renewable energy sources. The result is a liquid hydrocarbon fuel similar to gasoline or diesel, but with the potential to achieve carbon neutrality when produced sustainably. Unlike biofuels, e-fuels do not compete with food supply and can be engineered for consistency and purity — two factors critical for motorsport.
Why motorsport cares about e-fuels
 Racing is more than speed; it is about spectacle, engineering, and pushing limits. Full electrification may not be feasible or desirable for every series, particularly those that rely on long endurance formats or where engine sound and heritage are central to the fan experience. E-fuels provide:
Racing is more than speed; it is about spectacle, engineering, and pushing limits. Full electrification may not be feasible or desirable for every series, particularly those that rely on long endurance formats or where engine sound and heritage are central to the fan experience. E-fuels provide:
- Lower net CO₂ emissions: If CO₂ used in production is recaptured, the cycle can reduce overall greenhouse gases.
- Compatibility: Teams can run existing combustion engines with minimal modifications, saving investment in entirely new platforms.
- High energy density: Compared to batteries, synthetic fuels allow longer stints and quicker refueling, vital for endurance racing.
- Heritage preservation: Racing can keep its noise, character, and mechanical excitement while evolving to meet climate goals.
Challenges of synthetic fuels
Despite the excitement, several challenges stand between e-fuels and mass adoption in racing:
- Cost: Producing synthetic fuel today is expensive due to energy demands and limited facilities.
- Efficiency losses: Transforming renewable energy into hydrogen, then into liquid fuel, and finally burning it in engines involves multiple conversion steps with energy loss at each stage.
- Infrastructure: Global supply chains and trackside fueling systems must adapt to distribute e-fuels consistently.
- Lifecycle assessment: The environmental benefits depend on how the hydrogen is generated and whether CO₂ capture is genuinely sustainable.
Which racing series are testing synthetic fuels?
Several high-profile championships have already begun exploring e-fuels:
- Formula 1: Committed to running on 100% sustainable fuels by 2026, with e-fuels a central candidate.
- Dakar Rally: Testing biofuels and synthetic alternatives to handle extreme off-road conditions.
- Endurance series: GT and Le Mans categories are experimenting with blends to prepare for stricter emissions rules.
- National touring series: Several touring car championships are piloting synthetic fuel blends for domestic competitions.
How synthetic fuels affect race car engineering
 Switching to synthetic fuels isn’t a simple fill-up. Engineers must adapt cars to ensure performance and safety:
Switching to synthetic fuels isn’t a simple fill-up. Engineers must adapt cars to ensure performance and safety:
- Engine calibration: Adjusting ignition timing and compression to optimize combustion.
- Material compatibility: Checking seals, injectors, and tanks against possible new chemical compositions.
- Thermal behavior: Understanding how e-fuels burn under extreme conditions of racing.
- Durability testing: Running prototypes to confirm consistent performance across race distances.
Advantages for fans and sponsors
Beyond engineering, synthetic fuels could reshape motorsport’s public image:
- Fans: Keep the sounds and sensations of combustion engines while aligning with greener values.
- Sponsors: Attract eco-conscious partners keen to be associated with sustainability innovations.
- Manufacturers: Use racing as a testbed for fuel technologies that can later reach consumer markets.
Steps toward mainstream adoption
- Pilot projects: Limited classes using e-fuels to validate performance.
- Hybrid blends: Early adoption with partial blends to reduce emissions without full transition.
- Regulatory frameworks: Motorsport governing bodies setting timelines for adoption.
- Investment in production: Scaling plants to make fuel affordable and available worldwide.
- Partnerships: Alliances between fuel companies, automakers, and racing organizations.
Internal links
For more motorsport technology insights, explore related posts:
How to Choose the Right Tires for Track Days |
The Best Performance Mods to Upgrade Your Race Car |
Why Safety Is Crucial in Motorsport
Conclusion
Synthetic fuels are not a silver bullet, but they are a promising bridge between racing’s heritage and a sustainable future. They offer a way to maintain the thrill of combustion engines while meeting global emissions goals. Cost, efficiency, and infrastructure challenges remain, but with Formula 1 and endurance racing leading the charge, e-fuels may be commonplace on the grid by 2026. For motorsport fans, that means the roar of engines may continue — only cleaner.
Want the latest updates on racing technology? Subscribe to Daily Auto Sport or contact us here with your questions.


